Today’s Outline
- Defining a Function
- Calling a Function
- Declare a Function
- Passing Parameters
- Recursive Functions
Defining a Function
void printHello (int n) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cout << "Hello" << endl;
}
}
Calling a Function
void main() {
int x = 4;
printHello(x);
}
Function in C++ Library
#include <cmath> - Mathematical Calculations#include <cstring> - String Manipulations#include <iostream> - Input/Output
Function in Memory Stack

Declare a Function
Function Prototype
int findMax(int, int); // Function Prototype
void main() {
cout << findMax(3, 4);
}
int findMax(int x, int y) {
return x > y ? x : y;
}
- The function must be declared before use
- The function prototype is the declaration of the function
- The implementation of the function can be defined later
- Contains function prototype only
- To be included in the program that will call the function
Implementation file (.cpp)
- Contains function implementation
Passing Parameters
Argument vs Parameter
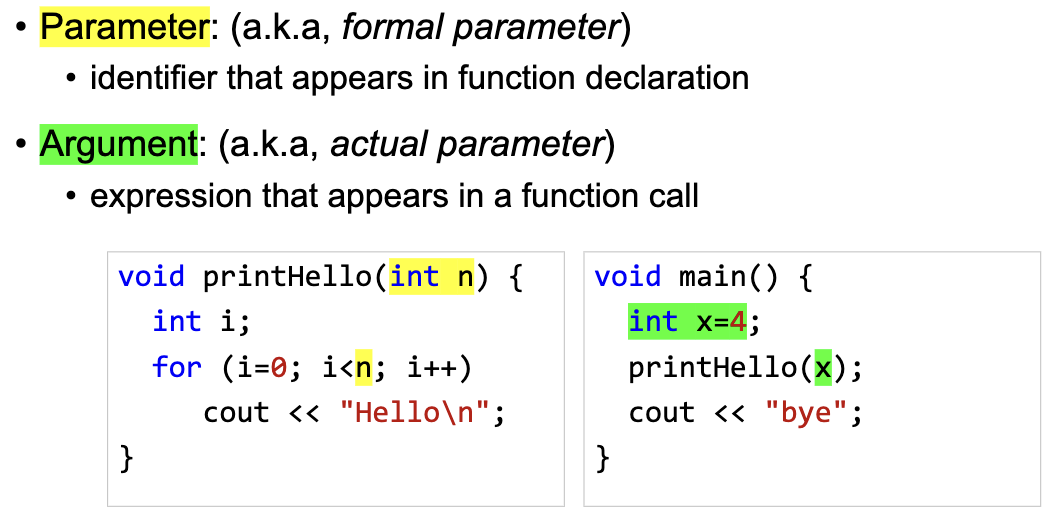
Parameter Passing in C++
- Pass-by-Value
- Pass-by-Reference
- Pass-by-Pointer (Later)
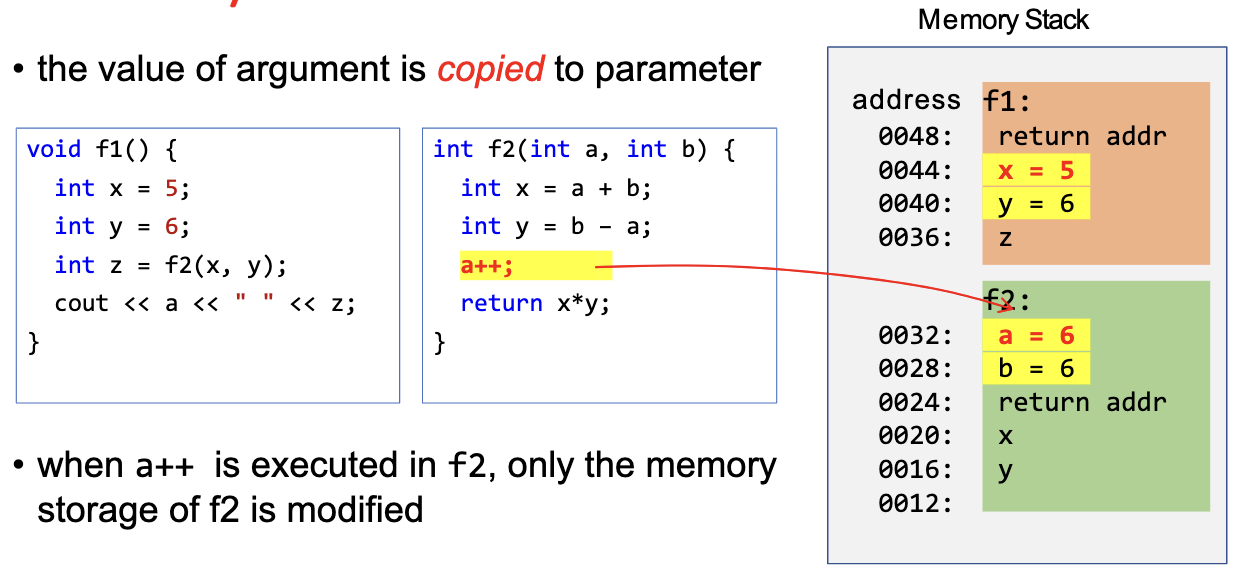
Pass-by-Value
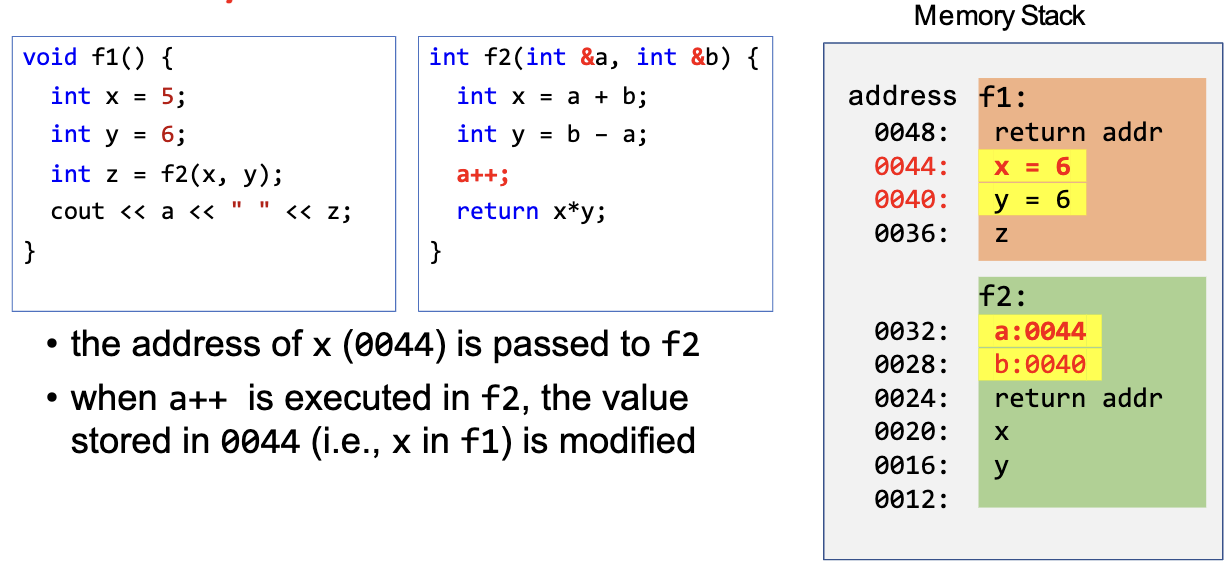
Pass-by-Reference
Parameter Passing: Default Parameters
void f(int a, int b = 0) {
cout << a << " " << b << endl;
}
- Default parameters must be defined from the last parameter
Recursive Functions
Iterative vs Recursive
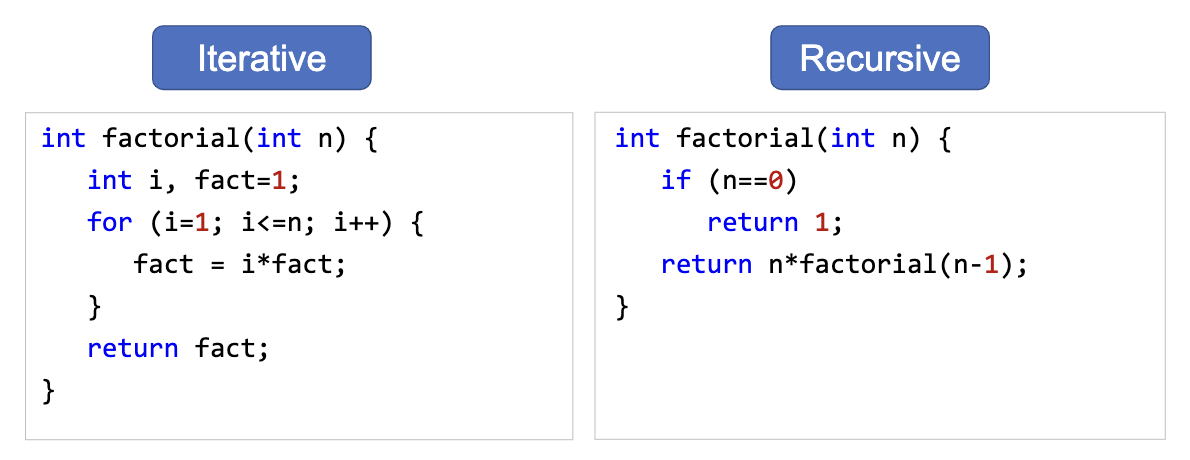
Efficiency of Recursion
- Generally speaking, non-recursive versions will execute more efficiently (time/space)
Summary
- Define, call, and declare functions
- Parameter passing
- Recursive functions




