AWS Overview
AWS Regions
- Region 이란 Cluster of Data Centers
us-east1,eu-west-3,ap-east-1, …
- 대부분의 AWS Services 는 특정 Region 에 국한됨
- Region 을 선택할 때 고려할 사항
- Compliance: Data 가 특정 지역을 벗어나면 안 될 경우
- Proximity: 가까운 Region 일수록 Latency 가 낮음
- Available Services: 모든 Region 이 모든 Service 를 지원하지 않음
- Pricing: Region 마다 요금이 다를 수 있음
AWS Availability Zones
- 각 Region 은 보통 3개에서 많게는 6개의 AZs 를 가지고 있음
ap-east-1a,ap-east-1b,ap-east-1c
- 각 AZ 는 여분의 전원, 네트워킹, 통신 기능을 갖춘 1개 이상의 데이터 센터로 이루어져 있음
- 정확한 숫자는 AWS 가 공개하지 않음
- 재난에 대비해 서로 분리되어 있는 것
- 각 AZ 들은 High bandwidth 와 Ultra-low latency networking 으로 연결되어 Region 을 형성
AWS Points of Presence (Edge Locations)
- AWS 는 400개 이상의 Points of Presence (400+ Edge Locations & 10+ Regional Caches) 을 40여 국가의 90개 이상의 도시에 가지고 있음
- 이를 통해 low latency 로 end user 에게 컨텐츠를 전달할 수 있음
AWS Services
- Global Services
- IAM
- R53 (DNS)
- CloudFront (CDN)
- WAF
- Regional Services
- EC2 (IaaS)
- EB (PaaS)
- Lambda (FaaS)
- Rekognition (SaaS)
Choosing the right DB
Database Types
- RDBMS: RDS, Aurora - great for joins
- NoSQL DB: No joins, no SQL - DynamoDB(~JSON), ElastiCache(key/value pairs), Neptune(graphs), DocumentDB(for MongoDB), Keyspaces(for Apache Cassandra)
- Object Store: S3(for big objects), Glacier(for backups/archives)
- Data Warehouse: Redshift(OLAP), Athena, EMR
- Search: OpenSearch(JSON) - free text, unstructured searches
- Graphs: Neptune - displays relationships between data
- Ledger: Quantum Ledger DB
- Time Series: Timestream
RDS
- Managed PostgreSQL / MySQL / Oracle / SQL Server / MariaDB / Custom
- Provisioned RDS instance size and EBS volume type & size
- Auto-scaling capability for storage
- Support for Read Replicas and Multi-AZ
- Security through IAM, SGs, KMS, and SSL in transit
- Automated Backup with Point in time restore feature (up to 35 days)
- Manual DB snapshot for longer-term recovery
- Support for IAM Authentication, integration with Secrets Manager
- RDS Custom for access to and customize the underlying instance (Oracle & SQL Server)
- Use case: Store RDBMS/OLTP, perform SQL queries, transactions
Aurora
- Compatible API for PostgreSQL / MySQL, separation of storage and compute
- Storage: data is stored in 6 replicas across 3 AZs
- Compute: Cluster of DB instances across multiple AZs, auto-scaling of Read Replicas
- Cluster: Custom endpoints for writer and reader DB instances
- Same security/monitoring/maintenance features as RDS
- Aurora Serverless: for unpredictable/intermittent workloads, no capacity planning
- Aurora Global: up to 16 DB Read Instances in each region, < 1 second storage replication
- Aurora Machine Learning: perform ML using SageMaker & Comprehend on Aurora
- Aurora DB Cloning: new cluster from existing one, faster than restoring a snapshot
- Use case: same as RDS, but with less maintenance/more flexibility/performance/features
ElastiCache
- Managed Redis / Memcached
- In-memory data store, sub-millisecond latnency
- Must provision an EC2 instance type
- Support for clustering(Redis) and Multi-AZ, Read Replicas(sharding)
- Security through IAM, SGs, KSM, Redis Auth
- Backup / Snapshot / Point in time restore feature
- Managed and Scheduled maintenance
- Requires some application code changes to be leveraged
- Use case: Key/Value store, frequent reads, less writes, cache results for DB queries, store session data for websites, cannot use SQL
DynamoDB
- AWS proprietary technology, managed serverless NoSQL DB, millisecond latency
- Capacity modes: provisioned capacity with optional auto-scaling or on-demand capacity
- Can replace ElastiCache as a Key/Value store
- HA, Multi-AZ by default, Read and Writes are decoupled, transaction capability
- DAX cluster for read cache, microsecond read latency
- Security, authentication, and authorization are done through IAM
- Event Processing: DDB Streams to integrate with Lambda, Kinesis Data Streams
- Global Table feature: active-active setup
- Automated backups up to 35 days with PITR, or on-demand backups
- Export to S3 without using RCU within the PITR window, import from S3 without using WCU
- Great to rapidly evolve schemas
- Use case: Serverless applications development (small documents 100s KB), distributed serverless cache
S3
- A key/value store for objects
- Great for bigger objects, not so great for many small objects
- Serverless, scales infinitely, max object size is 5TB, versioning capability
- Tiers: Standard, IA, Intelligent, Glacier + lifecycle policy
- Features: Versioning, Encryption, Replication, MFA-Delete, Access Logs, …
- Security: IAM, Bucket Policies, ACL, Access Points, Object Lambda, CORS, Object/Vault Lock
- Encryption: SSE-S3, SSE-KMS, SSE-C, client-side, TLS in transit, default encryption
- Batch operations on objects using S3 Batch, listing files using S3 Inventory
- Performance: Multi-part upload, S3 Transfer Acceleration, S3 Select
- Automation: S3 Event Notifications (SNS, SQS, Lambda, EventBridge)
- Use Cases: Static files, key-value store for big files, website hosting
DocumentDB
- AWS implementation for MongoDB(NoSQL DB)
- Used to store, query, and index JSON data
- Similar “deployment concept” to Aurora
- Fully managed, HA with replication across 3 AZ
- Document DB storage automatically grows in increments of 10GB
- Automatically scales to workloads with millions of requests per second
Neptune
- Fully managed graph DB
- e.g. Social network
- Users have friends
- Posts have comments
- Comments have likes from users
- Users share and like posts
- e.g. Social network
- HA across 3 AZ, with up to 15 read replicas
- Build and run applications working with highly connected datasets - optimized for these complex and hard queries
- Can store up to billions of relations and query the graph with millisecond latency
- Great for knowledge graphs (Wikipedia), fraud detection, recommendation engines, social networks
Keyspaces(for Apache Cassandra)
- Apache Cassandra is an open-source NoSQL distributed DB
- A managed Apache Cassandra-compatible DB service
- Serverless, scalable, HA
- Automatically scale tables up/down based on the app traffic
- Tables are replicated 3 times across multi-AZ
- Using the Cassandra Query Language (CQL)
- Single-digit millisecond latency at any scale, 1000s of requests per second
- Capacity: On-demand mode or provisioned mode with auto-scaling
- Encryption, backup, PITR up to 35 days
- Use case: Store IoT device info, time-series data, …
QLDB
- A ledger is a book recording financial transactions
- Fully managed, serverless, HA, replication across 3 AZs
- Used to review the history of all the changes made to your application data over time
- Immutable system: no entry can be removed or modified, cryptographically verifiable
- 2-3x better performance than common ledger blockchain frameworks, manipulate data using SQL
- Difference with Amazon Managed Blockchain: no decentralization component, in accordance with financial regulation rules
Timestream
- Fully managed, fast, scalable time series DB
- Automatically scales up/down to adjust capacity
- Store and analyze trillions of events per day
- 1000s times faster & 1/10 the cost of RDBMS
- Scheduled queries, multi-measure records, SQL compatibility
- Data storage tiering: recent data kept in memory and historical data kept in a cost-optimized storage
- Built-in time series analytics functions
- Encryption in transit and at rest
- Use cases: IoT apps, operational apps, real-time analytics, …
Review
-
S3 Transfer Acceleration = Edge Location 으로 transfer 해서 transfer speed 올리는 법
-
PrincipalOrgID = AWS Organization member accounts 만 접근 가능하게 for resource policies
-
Secrets Manager vs Parameter Store
- Secrets Manager = Auto Rotation
-
CloudFront vs Global Accelerator (both support Shield for DDoS)
- CloudFront = CDN for fast static content delivery, dynamic content (API acceleration)
- Origin = S3, ALB, EC2, HTTP backend
- Global Accelerator = Best routing by using Edge Locations
- TCP/UDP, MQTT(IoT), VoIP, HTTP with static IP address
- Provides static IP
- CloudFront = CDN for fast static content delivery, dynamic content (API acceleration)
-
Network Firewall = provides filtering for both inbound and outbound network traffic
-
GLB = L3 (IP Packets)
-
EBS Fast Snapshot Restore (FSR) = no latency on first use
-
SSO + MSAD = two-way forest trust AWS Directory Service for MSAD
-
AWS Config rules = to check resources that are not properly tagged
-
AWS Shield Advanced = ELB, CF, GA, R53
-
DR RPO/RTO order
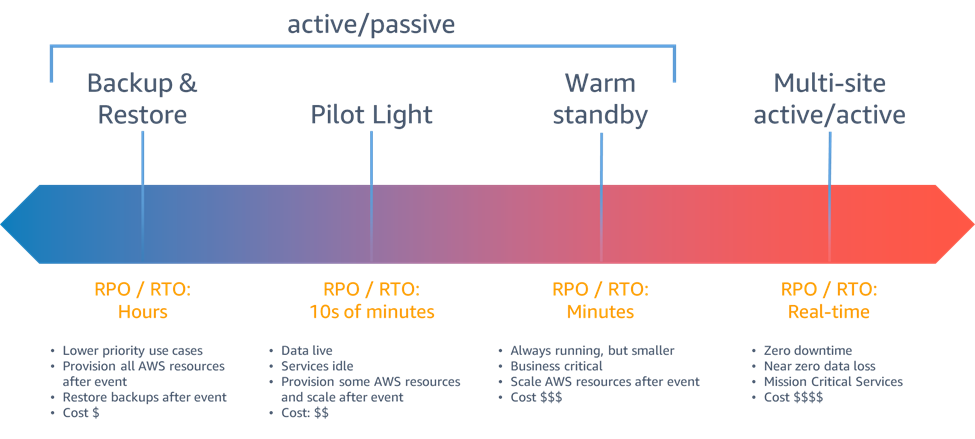
-
DDB PITR vs AWS Backup
- PITR = recover table to any point in time in a rolling 35 day window
- Backup = for long-term archiving and retention
-
Glue Job Bookmarks = prevent re-processing old data
-
S3 Legal Hold
- Protect the object indefinitely, independent from the retention period
- Can be freely placed and removed using the
s3:PutObjectLegalHoldIAM permission
-
Control Tower & SCPs can prevent VPCs from having access to Internet
-
CloudFront field-level encryption = allow to protect sensitive information throughout the application stack
-
Storage Gateway = iSCSI
- S3 File GW = extend storage space by leveraging Amazon S3, supports SMB
- FSx File GW?
- Volume GW
- stored volumes = your primary data is stored locally and your entire dataset is available for low-latency access while asynchronously backed up to AWS
- cached volumes = your primary data is written to S3, while retaining your frequently accessed data locally in a cache for low-latency access
- Tape GW?
-
S3 signed cookies & signed URLs for who do not have cookie support or unable to change hardcoded URLs
-
Compute Savings Plan vs EC2 Instance Savings Plan
- EC2 Instance Savings Plan = EC2 only & instance family committed
-
S3 Storage Lens
- Identify S3 buckets that are no longer being accessed or are rarely accessed
- Identify versioning enabled
-
S3 Inventory Report = List of unencrypted objects
-
SQS FIFO vs SQS
- FIFO = more expensive, guarantees processing exactly once
- Standard = at least once
-
FSx
- Amazon FSx for Lustre = SMB
- Amazon FSx for OpenZFS = NFS
- Amazon FSx for NetApp ONTAP = NFS, SMB, iSCSI
-
Lambda reserved concurrency vs provisioned concurrency
- reserved concurrency?
- provisioned concurrency
- SnapStart for Java can improve startup performance for latency-sensitive applications by up to 10x at no extra cost
-
Direct Connect vs VPN vs PrivateLink?
- PrivateLink with VPC endpoint allows to connect services across different accounts and VPCs
-
GW VPC Endpoint vs Interface VPC Endpoint
- GW Endpoint = for S3 and DDB, doesn’t allow from on-prem, peered VPCs in other Regions, or TGW
-
Kinesis Firehose vs Streams
-
io vs gp
- gp2 vs gp3 = gp3 is cheaper and better
- io1/2 supports Multi-Attach
-
Global, Reduce latency, health checks, no failover = Amazon CloudFront
-
Global ,Reduce latency, health checks, failover, Route traffic = Amazon Route 53
-
Use Workload Discovery on AWS to generate architecture diagrams of the workloads
-
Transfer Family supports AS2
-
Amazon S3 Glacier:
- Expedited Retrieval: Provides access to data within 1-5 minutes.
- Standard Retrieval: Provides access to data within 3-5 hours.
- Bulk Retrieval: Provides access to data within 5-12 hours.
-
Amazon S3 Glacier Deep Archive:
- Standard Retrieval: Provides access to data within 12 hours.
- Bulk Retrieval: Provides access to data within 48 hours.
-
X-Ray = trace the requests between the microservices