What is Splunk?
Splunk is a unified data platform that allows teams to work together or individually to ensure mission-critical digital systems stay secure and reliable.
Splunk’s primary features make your machine data available, accessible, and usable to everyone in your organization.
Index
Indexcontainsmachine datafrom servers, network devices, and web appsIndexerinspects enteringmachine dataand processes it and labels the data with asourcetype, when they find a match- Timestamps are identified and normalized to a consistent format
- Once data is ingested into the
index, it is available for searching and analysis
Using Splunk Web
After logging into Splunk Enterprise, you’ll be redirected to the Splunk Home app.
Apps are pre-configured environments that sit on top of your Splunk instance, extending its pre-built knowledge and capabilities.
Apps
- Apps are like workspaces built to solve a specific use case
- Apps are available on
Splunkbaseor can be defined by anadminuser- e.g.
- Search & Reporting
- Splunk Essentials for Cloud and Enterprise 9.0
- Splunk Secure Gateway
- e.g.
Roles
- Roles determine what a user can see, do, and interact with
- 3 pre-defined default roles in Splunk Enterprise:
- Admin Role: The most powerful role
- Install apps
- Ingest data
- Create knowledge objects for all users
- Power Role
- Create and share
knowledge objectswith all users of an app - Perform real-time searches
- Create and share
- User Role
- Only see their
knowledge objectsand those that have been shared with them
- Only see their
- Admin Role: The most powerful role
- Roles in Splunk Cloud:
- sc_admin
- power
- user
- additional cloud-specific roles
Data Summary
- Hosts: The hostname, IP address, or fully qualified domain name of the machine
- Sources: The file or directory path, network port, or script
- Sourcetypes: Classification of data
Using Search
- Limiting a search by time is key to faster results and is a best practice
- By default, a search job will remain active for 10 minutes
- Shared search jobs remain active for 7 days
- Search Mode
- Fast Mode
- Field discovery OFF for event searches
- No event or field data for stats searches
- Smart Mode
- Field discovery ON for event searches
- No event or field data for stats searches
- Verbose Mode
- All event & field data
- Fast Mode
Exploring Events
- Events are returned in
reverse chronological order - Time is normalized in your index to a consistent format
- The timestamp of the event is based on the time zone set in the user account
Using Search Terms
Search Terms
- Wildcard
(*)can be used- e.g.
fail*return events containingfail,failure,failed
- e.g.
- Search terms are not case-sensitive
- e.g.
failedandFAILEDwill return the same results
- e.g.
- Exact phrases can be searched with quotes
- e.g.
"failed password" - Search terms containing quotes can be escaped with backslashes
- e.g.
"user \"chrisV4\" not in database"
- e.g.
- e.g.
Booleans
AND,OR, andNOTcan be used in the search terms- Boolean operations have an order of evaluation in order of:
NOTORAND
- Parentheses can be used to control the order of evaluation
- e.g.
failed NOT (success OR accepted)
- e.g.
Commands
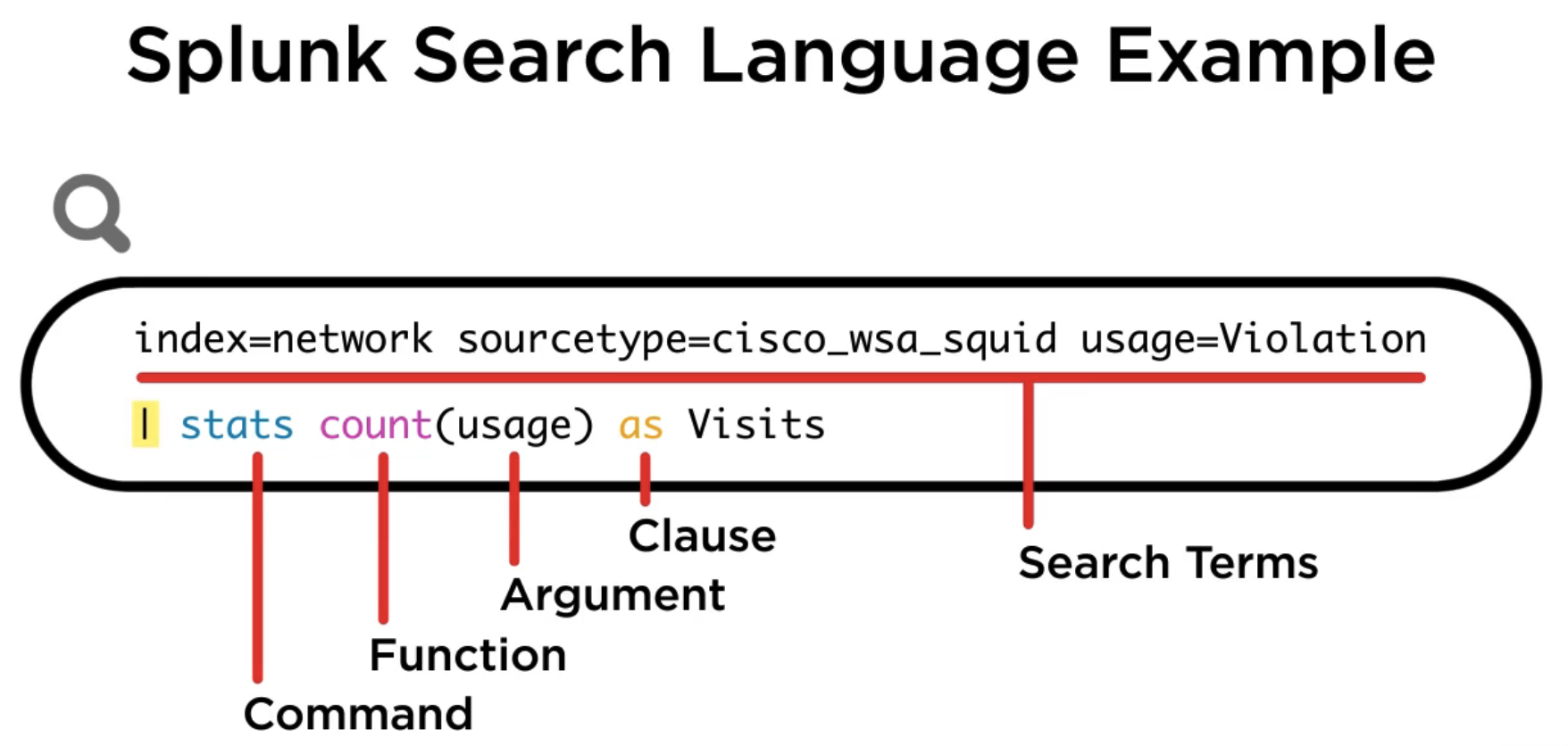 Splunk’s search language is built from 5 components:
Splunk’s search language is built from 5 components:
- Search Terms
- Commands
- Functions
- Arguments
- Clause
Best Practices
- If a command references a specific value, that value will be case-sensitive
- In order of
timeindexsourcehostsourcetypecan be used to filter events
Knowledge Objects
Knowledge objectsare tools that help users discover and analyze dataKnowledge objectsare grouped into 5 categories:- Data Interpretation
- Fields
- Field Extractions
- Calculated Fields
- Data Classification
- Event Types
- Transactions
- Data Enrichment
- Lookups
- Workflow Actions
- Data Normalization
- Tags
- Field Aliases
- Data Models (Search-time mapping of knowledge)
- Hierarchically-structured datasets
- Data Interpretation