DNS 란
DNS Terminologies
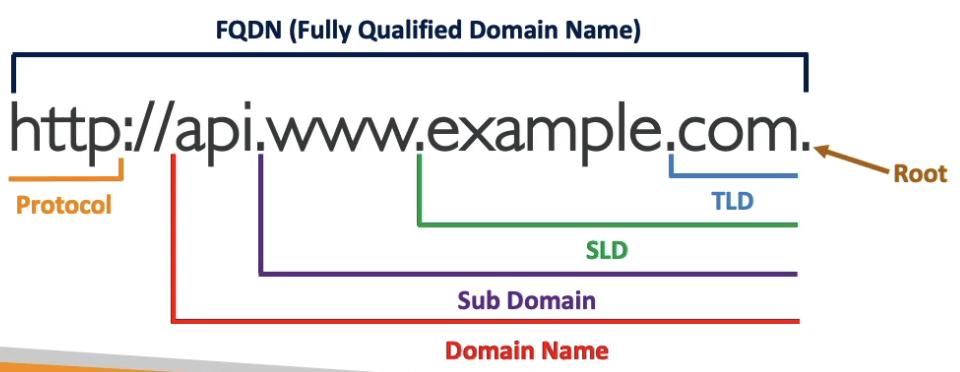
- Domain Register: Amazone Route 53, GoDaddy, …
- DNS Records: A, AAAA, CNAME, NS, …
- Zone File: Contains DNS records
- Name Server: Resolves DNS queries (Authoritative or Non-Authoritative)
- Top Level Domain (TLD):
.com, .gov, .org, …
- Second Level Domain (SLD):
amazon.com, google.com, …
How DNS works
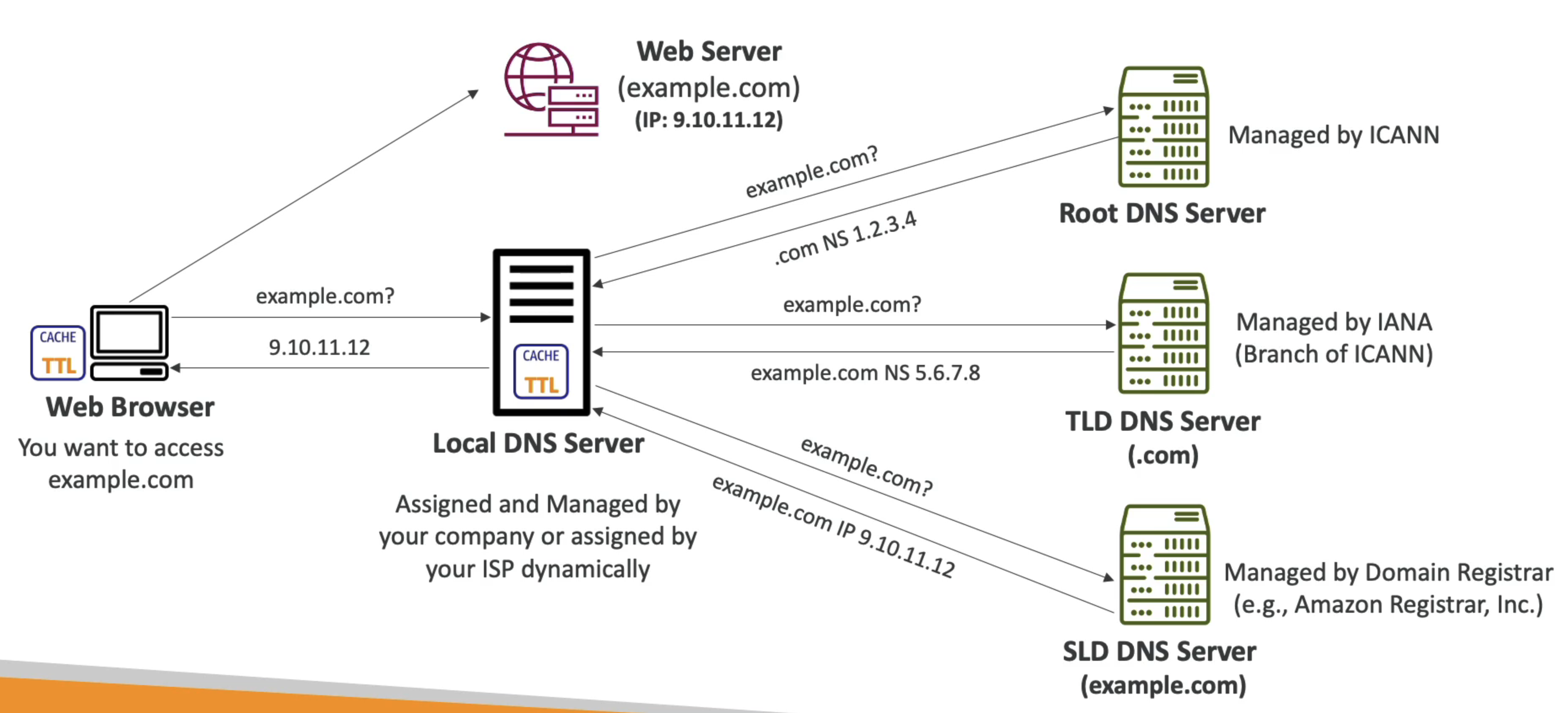
Amazon Route 53
- A HA, scalable, fully managed, and Authoritative DNS
- Authoritative: Customer can update the DNS records
- R53 is also a Domain Register
- Health-check available
- The only AWS service that provides 100% availability SLA
Records
- How you want to route traffic for a domain
- Each record contains:
- Domain/Subdomain Name: e.g. example.com
- Record Type: e.g. A or AAAA
- Value: e.g. 123.456.789.123
- Routing Policy: How R53 responds to queries
- TTL: Amount of time the record cached at DNS Resolvers
- R53 supports the following DNS record types:
- A / AAAA / CNAME / NS
- (Advanced) CAA / DS / MX / NAPTR / PTR / SOA / TXT / SPF / SRV
Record Types
- A: maps a hostname to IPv4
- AAAA: maps a hostname to IPv6
- CNAME: maps a hostname to another hostname
- The target is a domain name which must have an A or AAAA record
- Cannot create a CNAME record for the top node of a DNS namespace (Zone Apex)
- NS: Name Servers for the Hosted Zone
- Control how traffic is routed for a domain
CNAME vs Alias
- AWS Resources (LB, CloudFront, …) expose an AWS hostname
- CNAME
- Points a hostname to any other hostname (app.domain.com ⇒ any.thing.com)
- Only for non-root domain (sub.domain.com)
- Alias
- Points a hostname to an AWS Resources (app.domain.com ⇒ any.amazonaws.com)
- Works for the root domain and non-root domain (domain.com)
- Free of charge
- Native health-check
Alias Records
- Maps a hostname to an AWS resource
- An extension to DNS functionality
- Automatically recognizes changes in the resource’s IP addresses
- Unlike CNAME, it can be used for the top node of a DNS namespace (Zone Apex)
- Alias Record is always of type A/AAAA for AWS resources (IPv4/IPv6)
- Cannot set TTL
- Alias Records Targets
- ELB
- CloudFront Distributions
- API Gateway
- EB Environments
- S3 Websites
- VPC Interface Endpoints
- Global Accelerator’s Accelerator
- R53 Record in the same hosted zone
- But cannot set for EC2 DNS name
Hosted Zones
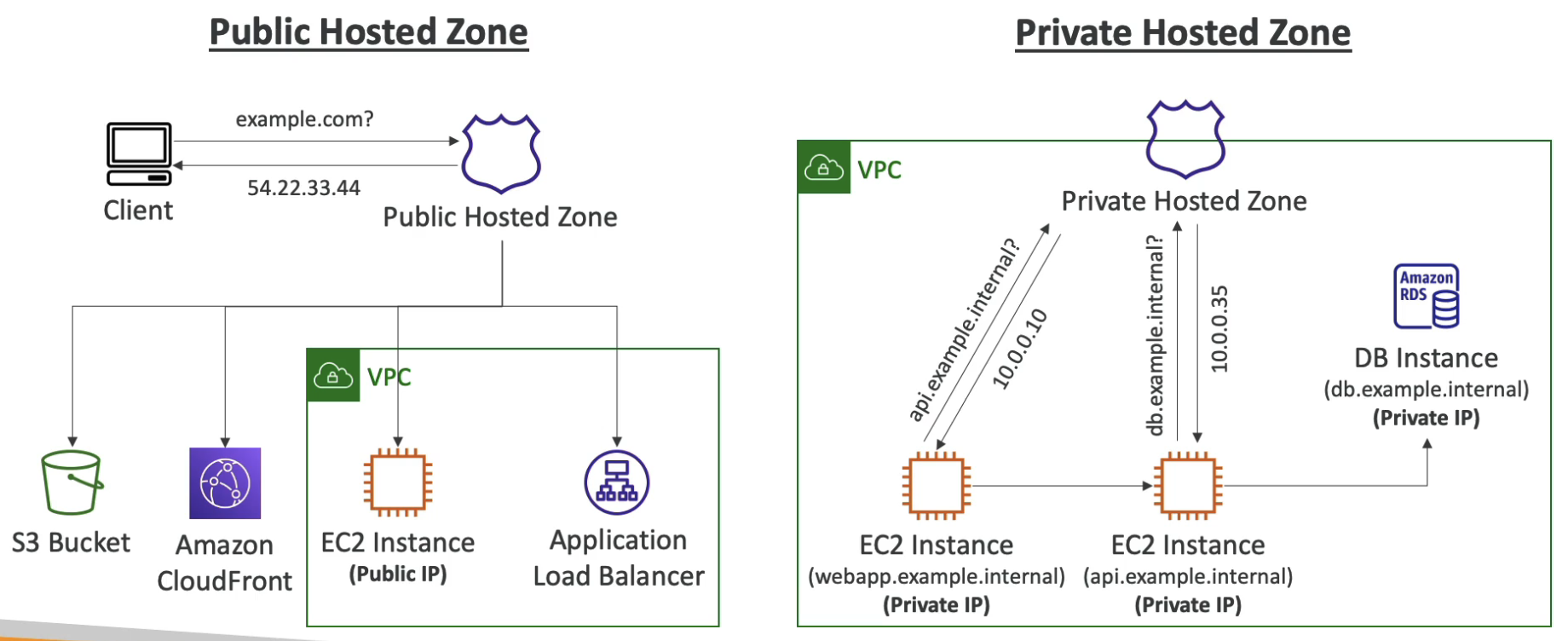
- A container for records that define how to route traffic to a domain and its subdomains
- Public Hosted Zones - contains records that specify how to route traffic on the internet (public domain names)
- Private Hosted Zones - contains records that specify how you route traffic within one or more VPCs (private domain names)
- $0.5 per month per hosted zone
Resolver Endpoints
- Inbound Endpoint
- On-premises 네트워크에서 들어오는 DNS 쿼리를 처리하는 VPC 의 엔드포인트
- VPC 내의 도메인 이름에 대한 DNS 쿼리를 처리하는 데 사용
- On-premises DNS Resolver 가 DNS 쿼리를 R53 Resolver 로 전달 가능
- On-premises DNS Resolver 가 R53 Private Hosted Zone 에서 AWS 리소스 및 레코드에 대한 도메인 이름 확인 가능
- Outbound Endpoint
- VPC 에서 On-premises 네트워크로 DNS 쿼리를 전달하는 VPC 의 엔드포인트
Health Checks
- HTTP Health Checks are only for Public Resources
- Health Check → Automated DNS Failover:
- Health Checks that monitor an endpoint (application, server, other AWS resources)
- About 15 global Health Checkers will check the endpoint health
- Health Checks pass only when the endpoint responds with the 2xx or 3xx
- Health Checks can be set up to pass/fail based on the text in the first 5120 bytes of the response
- Health Checks that monitor other health checks (Calculated Health Checks)
- Combine the results of multiple Health Checkers into a single Health Check
- Used to perform maintenance to a website without causing all health checks to fail
- Health Checks that monitor CloudWatch Alarms
- R53 Health Checkers are outside the VPC
- CW metric and associate CW alarm to Health Check the alarm
- Health Checks are integrated with CloudWatch metrics
Routing Policies
- Define how R53 responds to DNS queries
- R53 supports the following Routing Policies
- Simple
- Weighted
- Failover
- Latency-based
- Geolocation
- Multi-Value Answer
- Geoproximity (using R53 Traffic Flow feature)
Simple
- Typically, route traffic to a single resource
- Can specify multiple values in the same record
- A random one is chosen by the client
- When Alias is enabled, specify only 1 AWS resource
- Can’t be associated with Health Checks
Weighted
- Control the % of the requests that go to each specific resource
- Assign each record a relative weight
- DNS records must have the same name and type
- Can be associated with Health Checks
- Assign a weight of 0 to a record to stop sending traffic
- If all records have weight of 0, then all records will be returned equally
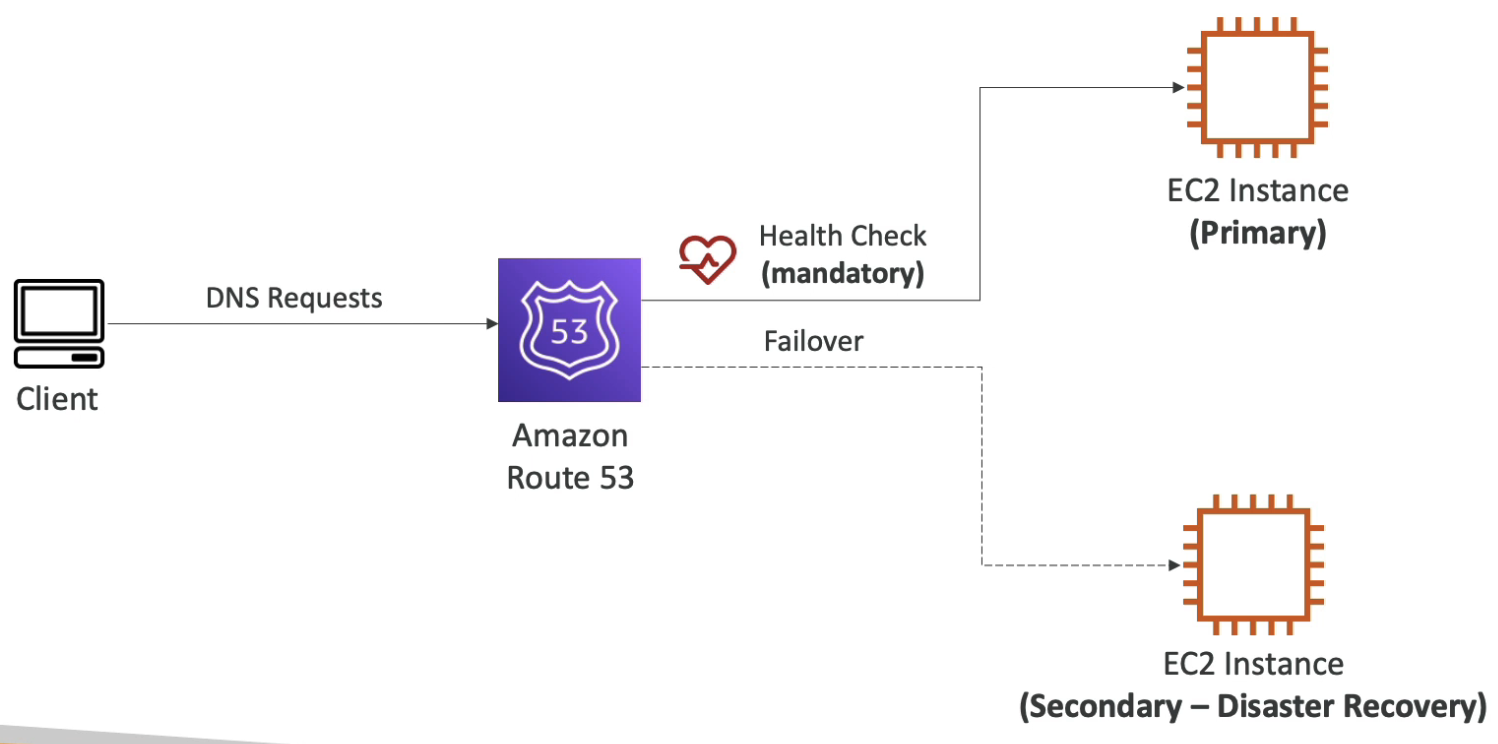
Failover
Latency-based
- Redirect to the resource that has the least latency close to the user
- Latency is based on traffic between users and AWS Regions
- Can be associated with Health Checks
Geolocation
- Different from Latency-based
- This routing is based on user location
- Specify location by Continent, Country or by US State
- Should create a “Default” record (in case there’s no match on location)
- Use cases: website localization, restrict content distribution, …
- Can be associated with Health Checks
Geoproximity
- Route traffic to resources based on the geographic location of users and resources
- Ability to shift more traffic to resources based on the defined bias
- To change the size of the geographic region, specify bias values:
- To expand (1 to 99) - more traffic to the resource
- To shrink (-1 to -99) - less traffic to the resource
- Must use R53 Traffic Flow (advanced) to use this feature
IP-based Routing
- Routing based on clients’ IP addresses
- Provide a list of CIDRs for clients and the corresponding endpoints/locations
- Use cases: Optimize performance, reduce network costs, …
- e.g. Route end users from a particular ISP to a specific endpoint
Multi-Value
- User when routing traffic to multiple resources
- R53 returns multiple resources
- Can be associated with Health Checks
- Up to 8 healthy records are returned for each Multi-Value query
- Multi-Value is not a substitute for having an ELB
References



